Understanding Meniscus Tear Recovery
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/meniscusfinal-01-5c8fba21c9e77c00010e96f5.png)
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber in the knee joint. A meniscus tear occurs when this cartilage is torn, often due to a sudden twisting or impact injury. Recovery from a meniscus tear can vary depending on the severity of the tear and the chosen treatment option.
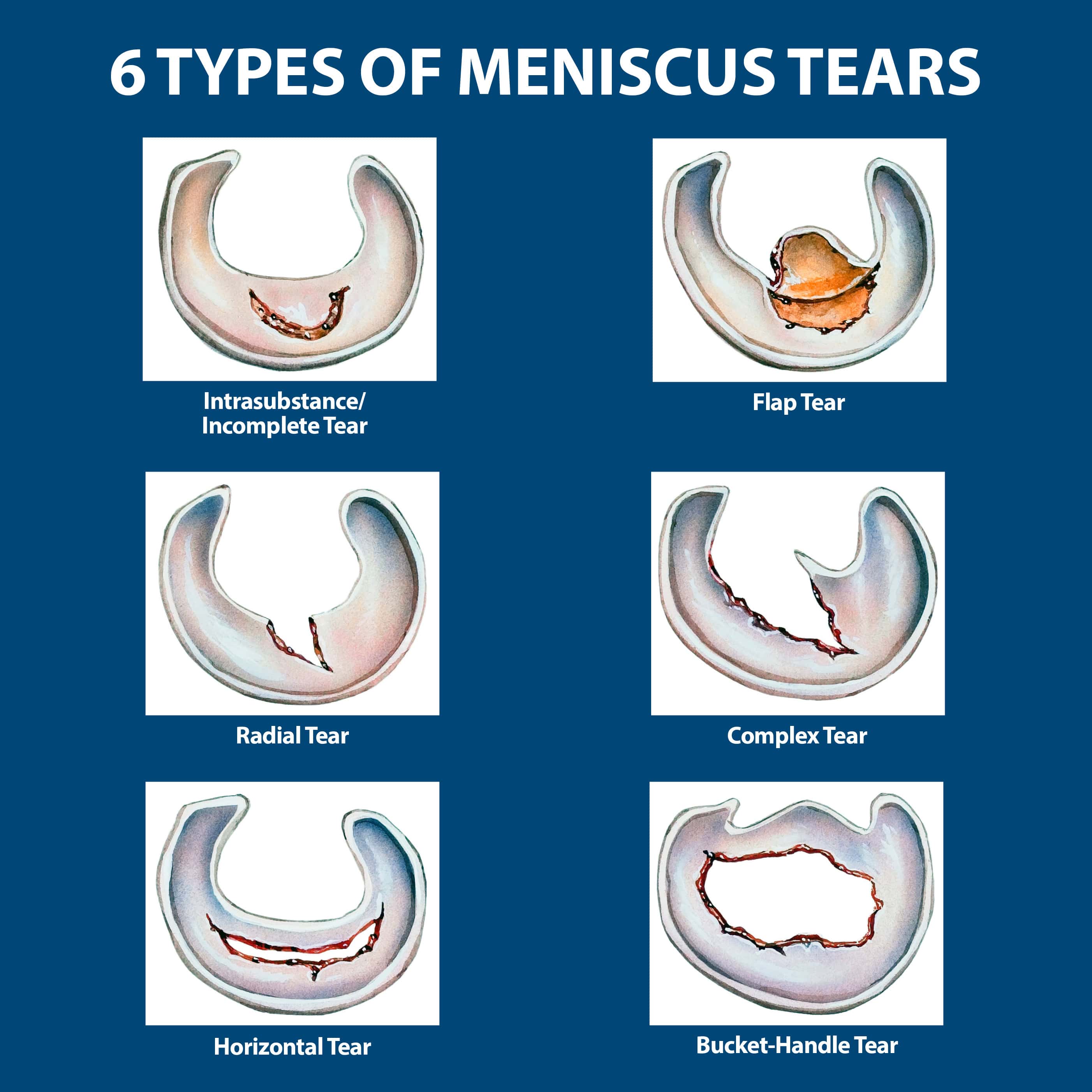
Types of Meniscus Tears
The type of meniscus tear can impact the recovery process. Tears are classified based on their location, size, and shape.
- Horizontal Tear: This tear runs across the width of the meniscus.
- Vertical Tear: This tear runs from the top to the bottom of the meniscus.
- Radial Tear: This tear is a more complex tear that runs in a radial pattern.
- Degenerative Tear: This type of tear occurs due to wear and tear on the meniscus over time, often seen in older individuals.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear
Common symptoms of a meniscus tear include:
- Pain: Sharp pain in the knee, especially during twisting or weight-bearing activities.
- Swelling: Swelling around the knee joint.
- Stiffness: Difficulty bending or straightening the knee.
- Locking: A feeling of the knee locking or catching.
- Clicking or popping: A clicking or popping sensation in the knee.
Healing Process for a Meniscus Tear
The healing process for a meniscus tear depends on the type and severity of the tear.
- Small Tears: Small tears may heal on their own with conservative treatment, such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) therapy, and pain medication.
- Large Tears: Large tears may not heal on their own and may require surgery.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for a meniscus tear can be broadly categorized as conservative or surgical.
Conservative Treatment
Conservative treatment options are often the first line of treatment for meniscus tears. These options aim to reduce pain and inflammation and allow the tear to heal naturally. Conservative treatment options may include:
- RICE Therapy: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen, or prescription pain medications.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve range of motion.
- Bracing: A knee brace can provide support and stability to the knee joint.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for a meniscus tear is typically considered when conservative treatment fails to relieve symptoms or for large tears that are unlikely to heal on their own. Surgical options include:
- Meniscectomy: This procedure involves surgically removing the torn portion of the meniscus.
- Meniscus Repair: This procedure involves stitching the torn portion of the meniscus back together. This is usually only possible for certain types of tears.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Meniscus Tear Recovery

A meniscus tear is a common injury that can occur in the knee. It happens when the meniscus, a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between the thighbone and shinbone, is torn. While surgery is sometimes necessary, many meniscus tears can be effectively treated without surgery.
RICE Therapy
RICE therapy is a common first-line treatment for meniscus tears. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This method helps reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
- Rest: Avoid activities that put stress on your knee. This means limiting weight-bearing activities and using crutches or a cane for support.
- Ice: Apply ice to the injured area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Ice helps reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage to help reduce swelling and support the knee.
- Elevation: Keep your leg elevated above your heart as much as possible. This helps reduce swelling by promoting fluid drainage.
Physical Therapy Exercises
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in meniscus tear recovery. Exercises help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve flexibility, and restore range of motion. A physical therapist will create a personalized exercise program based on the severity of your tear and your individual needs.
- Strengthening Exercises: Examples include quadriceps and hamstring strengthening exercises, such as leg extensions, hamstring curls, and calf raises.
- Flexibility Exercises: These exercises focus on improving the range of motion in the knee joint. Examples include knee flexion and extension exercises, and ankle pumps.
- Proprioceptive Exercises: These exercises help improve balance and coordination. Examples include standing on one leg, walking heel-to-toe, and performing single-leg squats.
Sample Rehabilitation Program
A sample rehabilitation program for a meniscus tear may include the following stages:
Stage 1: Initial Recovery (First 2-4 Weeks)
- RICE therapy to reduce pain and swelling.
- Gentle range of motion exercises to maintain flexibility.
- Non-weight-bearing exercises, such as ankle pumps and quadriceps sets.
Stage 2: Early Strengthening (Weeks 4-8)
- Continue RICE therapy as needed.
- Increase range of motion exercises.
- Begin weight-bearing exercises, such as walking and stationary cycling.
- Start light strengthening exercises for the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
Stage 3: Functional Strengthening (Weeks 8-12)
- Progress to more challenging strengthening exercises.
- Increase the intensity and duration of weight-bearing exercises.
- Begin sport-specific exercises.
Stage 4: Return to Activity (Weeks 12-16)
- Gradually return to your desired activity level.
- Continue to monitor your progress and listen to your body.
Pain Management and Medication
Pain management is an essential part of meniscus tear recovery. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications, such as opioids or muscle relaxants.
Surgical Treatment for Meniscus Tear Recovery
Surgery is often considered when conservative treatment options fail to provide adequate pain relief and functional improvement for a meniscus tear. Surgical procedures for meniscus tears aim to address the damaged tissue and restore joint stability.
Meniscectomy
Meniscectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the damaged portion of the meniscus. It is typically performed arthroscopically, a minimally invasive technique that uses small incisions and a camera to visualize the joint.
Benefits of Meniscectomy
- Pain relief: Removing the damaged portion of the meniscus can alleviate pain caused by the tear.
- Improved mobility: Removing the torn tissue can reduce friction and improve joint movement.
- Faster recovery: Compared to meniscus repair, meniscectomy often has a shorter recovery period.
Risks of Meniscectomy
- Joint instability: Removing a significant portion of the meniscus can increase the risk of joint instability.
- Increased risk of osteoarthritis: The meniscus plays a role in cushioning and stabilizing the knee joint. Removing a portion of it can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the future.
- Possible complications: Like any surgical procedure, meniscectomy carries the risk of complications, such as infection or bleeding.
Meniscus Repair
Meniscus repair is a surgical procedure that aims to suture the torn meniscus back together. It is typically performed arthroscopically and involves using sutures and anchors to reattach the torn edges.
Benefits of Meniscus Repair
- Preservation of joint function: Repairing the meniscus helps maintain the joint’s natural cushioning and stability.
- Reduced risk of osteoarthritis: Preserving the meniscus can help lower the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the future.
- Long-term stability: A successful meniscus repair can provide long-term stability and function to the knee joint.
Risks of Meniscus Repair
- Healing complications: The repair may not heal properly, leading to further tears or instability.
- Longer recovery time: Meniscus repair typically requires a longer recovery period compared to meniscectomy.
- Possible complications: Like any surgical procedure, meniscus repair carries the risk of complications, such as infection or bleeding.
Surgical Process
The surgical process for meniscus repair or meniscectomy typically involves the following steps:
Pre-operative Preparation
- Medical history and physical examination: A thorough medical history and physical examination are conducted to assess the patient’s overall health and the extent of the meniscus tear.
- Imaging studies: Imaging tests, such as MRI or X-ray, are used to confirm the diagnosis and determine the location and severity of the tear.
- Pre-operative instructions: The surgeon will provide specific instructions regarding fasting, medications, and other pre-operative preparations.
Surgical Procedure
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
- Arthroscopic surgery: Small incisions are made around the knee joint, and a thin, telescope-like instrument called an arthroscope is inserted. The arthroscope allows the surgeon to visualize the joint and perform the repair or removal of the torn meniscus.
- Repair or removal: Depending on the type of tear and the patient’s condition, the surgeon will either repair the torn meniscus using sutures and anchors or remove the damaged portion.
- Closure: Once the procedure is complete, the incisions are closed with sutures or staples.
Post-operative Care
- Pain management: Pain medication is prescribed to manage post-operative pain.
- Immobilization: The knee may be immobilized with a brace or sling for a period of time to allow for healing.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy is crucial for regaining strength, flexibility, and mobility after surgery. It typically involves a gradual progression of exercises, starting with range-of-motion exercises and progressing to strengthening and balance exercises.
- Weight-bearing restrictions: Weight-bearing restrictions may be imposed to protect the healing joint. These restrictions are gradually lifted as the knee heals.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing progress and address any concerns.
Importance of Post-operative Instructions and Physical Therapy, Meniscus tear recovery
Following post-operative instructions and attending physical therapy sessions are crucial for successful recovery after meniscus surgery.
- Proper healing: Following post-operative instructions helps ensure proper healing and reduces the risk of complications.
- Regaining function: Physical therapy plays a vital role in regaining strength, flexibility, and mobility after surgery. It helps restore joint function and improve overall knee health.
- Preventing future injuries: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, which can help prevent future injuries.
Meniscus tear recovery can be a long and arduous journey, demanding patience and perseverance. Just like justin jefferson had to work tirelessly to become a superstar, you too must commit to your rehabilitation program to regain full strength and mobility.
Remember, every step forward, no matter how small, brings you closer to a complete recovery.
Recovering from a meniscus tear can be a challenging journey, requiring patience and dedication. Just like Jahmyr Gibbs, a rising star in the NFL, jahmyr gibbs has shown resilience and determination in his own athletic pursuits, overcoming obstacles to achieve success.
Similarly, with the right care and commitment, you can conquer your meniscus tear and return to your active lifestyle.
